[Mlir-commits] [mlir] 39b9395 - [MLIR][Presburger] Add simplify function (#69107)
llvmlistbot at llvm.org
llvmlistbot at llvm.org
Sat Oct 28 03:55:49 PDT 2023
Author: gilsaia
Date: 2023-10-28T16:25:44+05:30
New Revision: 39b939555f959b93061b3c4c8fffc13a63737074
URL: https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/commit/39b939555f959b93061b3c4c8fffc13a63737074
DIFF: https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/commit/39b939555f959b93061b3c4c8fffc13a63737074.diff
LOG: [MLIR][Presburger] Add simplify function (#69107)
Added the simplify function to reduce the size of the constraint system,
referencing the ISL implementation.
Tested it on a simple Benchmark implemented by myself, calling SImplify
before the operation and calling Simplify on the result after Subtract
were tested, respectively.
The Benchmark can be found here:
[benchmark](https://github.com/gilsaia/llvm-project-test-fpl/blob/develop_benchmark/mlir/benchmark/presburger/Benchmark.cpp)
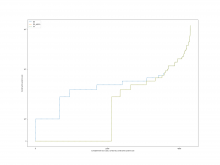
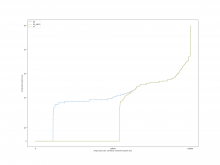
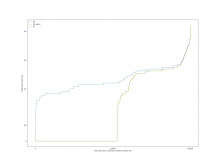
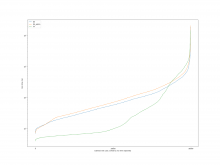
For the case of calling Simplify before each operation, the overall
result is shown in the following figure.

A comparison of the constraint system sizes and time for each operation
is as follows

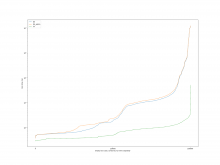
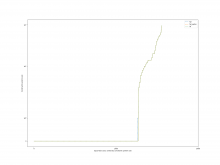
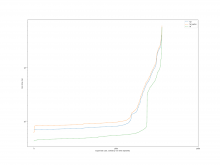

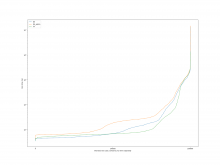
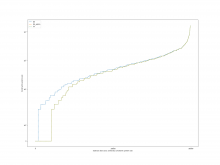
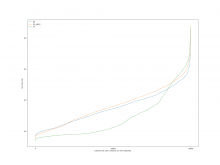
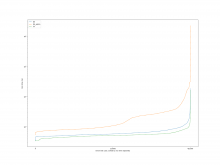
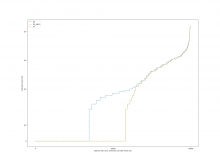
For the case of calling Simplify on the result after Subtract, the
overall results are as follows
A comparison of the constraint system sizes and time for subtract is as
follows
Added:
Modified:
mlir/include/mlir/Analysis/Presburger/IntegerRelation.h
mlir/include/mlir/Analysis/Presburger/PresburgerRelation.h
mlir/lib/Analysis/Presburger/IntegerRelation.cpp
mlir/lib/Analysis/Presburger/PresburgerRelation.cpp
Removed:
################################################################################
diff --git a/mlir/include/mlir/Analysis/Presburger/IntegerRelation.h b/mlir/include/mlir/Analysis/Presburger/IntegerRelation.h
index 56484622ec980cd..4c6b810f92e95af 100644
--- a/mlir/include/mlir/Analysis/Presburger/IntegerRelation.h
+++ b/mlir/include/mlir/Analysis/Presburger/IntegerRelation.h
@@ -91,6 +91,15 @@ class IntegerRelation {
return IntegerRelation(space);
}
+ /// Return an empty system containing an invalid equation 0 = 1.
+ static IntegerRelation getEmpty(const PresburgerSpace &space) {
+ IntegerRelation result(0, 1, space.getNumVars() + 1, space);
+ SmallVector<int64_t> invalidEq(space.getNumVars() + 1, 0);
+ invalidEq.back() = 1;
+ result.addEquality(invalidEq);
+ return result;
+ }
+
/// Return the kind of this IntegerRelation.
virtual Kind getKind() const { return Kind::IntegerRelation; }
@@ -138,7 +147,7 @@ class IntegerRelation {
/// returns false. The equality check is performed in a plain manner, by
/// comparing if all the equalities and inequalities in `this` and `other`
/// are the same.
- bool isPlainEqual(const IntegerRelation &other) const;
+ bool isObviouslyEqual(const IntegerRelation &other) const;
/// Return whether this is a subset of the given IntegerRelation. This is
/// integer-exact and somewhat expensive, since it uses the integer emptiness
@@ -351,6 +360,9 @@ class IntegerRelation {
/// Returns false otherwise.
bool isEmpty() const;
+ /// Performs GCD checks and invalid constraint checks.
+ bool isObviouslyEmpty() const;
+
/// Runs the GCD test on all equality constraints. Returns true if this test
/// fails on any equality. Returns false otherwise.
/// This test can be used to disprove the existence of a solution. If it
@@ -545,6 +557,10 @@ class IntegerRelation {
void removeDuplicateDivs();
+ /// Simplify the constraint system by removing canonicalizing constraints and
+ /// removing redundant constraints.
+ void simplify();
+
/// Converts variables of kind srcKind in the range [varStart, varLimit) to
/// variables of kind dstKind. If `pos` is given, the variables are placed at
/// position `pos` of dstKind, otherwise they are placed after all the other
@@ -724,6 +740,10 @@ class IntegerRelation {
/// Returns the number of variables eliminated.
unsigned gaussianEliminateVars(unsigned posStart, unsigned posLimit);
+ /// Perform a Gaussian elimination operation to reduce all equations to
+ /// standard form. Returns whether the constraint system was modified.
+ bool gaussianEliminate();
+
/// Eliminates the variable at the specified position using Fourier-Motzkin
/// variable elimination, but uses Gaussian elimination if there is an
/// equality involving that variable. If the result of the elimination is
@@ -755,6 +775,10 @@ class IntegerRelation {
/// equalities.
bool isColZero(unsigned pos) const;
+ /// Checks for identical inequalities and eliminates redundant inequalities.
+ /// Returns whether the constraint system was modified.
+ bool removeDuplicateConstraints();
+
/// Returns false if the fields corresponding to various variable counts, or
/// equality/inequality buffer sizes aren't consistent; true otherwise. This
/// is meant to be used within an assert internally.
diff --git a/mlir/include/mlir/Analysis/Presburger/PresburgerRelation.h b/mlir/include/mlir/Analysis/Presburger/PresburgerRelation.h
index 0c9c5cf67b4c3c1..c6b00eca90733a0 100644
--- a/mlir/include/mlir/Analysis/Presburger/PresburgerRelation.h
+++ b/mlir/include/mlir/Analysis/Presburger/PresburgerRelation.h
@@ -169,17 +169,17 @@ class PresburgerRelation {
bool isIntegerEmpty() const;
/// Return true if there is no disjunct, false otherwise.
- bool isPlainEmpty() const;
+ bool isObviouslyEmpty() const;
/// Return true if the set is known to have one unconstrained disjunct, false
/// otherwise.
- bool isPlainUniverse() const;
+ bool isObviouslyUniverse() const;
/// Perform a quick equality check on `this` and `other`. The relations are
/// equal if the check return true, but may or may not be equal if the check
/// returns false. This is doing by directly comparing whether each internal
/// disjunct is the same.
- bool isPlainEqual(const PresburgerRelation &set) const;
+ bool isObviouslyEqual(const PresburgerRelation &set) const;
/// Return true if the set is consist of a single disjunct, without any local
/// variables, false otherwise.
@@ -213,6 +213,10 @@ class PresburgerRelation {
/// also be a union of convex disjuncts.
PresburgerRelation computeReprWithOnlyDivLocals() const;
+ /// Simplify each disjunct, canonicalizing each disjunct and removing
+ /// redundencies.
+ PresburgerRelation simplify() const;
+
/// Print the set's internal state.
void print(raw_ostream &os) const;
void dump() const;
diff --git a/mlir/lib/Analysis/Presburger/IntegerRelation.cpp b/mlir/lib/Analysis/Presburger/IntegerRelation.cpp
index be764bd7c9176b9..a18947a04602a57 100644
--- a/mlir/lib/Analysis/Presburger/IntegerRelation.cpp
+++ b/mlir/lib/Analysis/Presburger/IntegerRelation.cpp
@@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ bool IntegerRelation::isEqual(const IntegerRelation &other) const {
return PresburgerRelation(*this).isEqual(PresburgerRelation(other));
}
-bool IntegerRelation::isPlainEqual(const IntegerRelation &other) const {
+bool IntegerRelation::isObviouslyEqual(const IntegerRelation &other) const {
if (!space.isEqual(other.getSpace()))
return false;
if (getNumEqualities() != other.getNumEqualities())
@@ -701,6 +701,12 @@ bool IntegerRelation::isEmpty() const {
return false;
}
+bool IntegerRelation::isObviouslyEmpty() const {
+ if (isEmptyByGCDTest() || hasInvalidConstraint())
+ return true;
+ return false;
+}
+
// Runs the GCD test on all equality constraints. Returns 'true' if this test
// fails on any equality. Returns 'false' otherwise.
// This test can be used to disprove the existence of a solution. If it returns
@@ -1079,6 +1085,57 @@ unsigned IntegerRelation::gaussianEliminateVars(unsigned posStart,
return posLimit - posStart;
}
+bool IntegerRelation::gaussianEliminate() {
+ gcdTightenInequalities();
+ unsigned firstVar = 0, vars = getNumVars();
+ unsigned nowDone, eqs, pivotRow;
+ for (nowDone = 0, eqs = getNumEqualities(); nowDone < eqs; ++nowDone) {
+ // Finds the first non-empty column.
+ for (; firstVar < vars; ++firstVar) {
+ if (!findConstraintWithNonZeroAt(firstVar, true, &pivotRow))
+ continue;
+ break;
+ }
+ // The matrix has been normalized to row echelon form.
+ if (firstVar >= vars)
+ break;
+
+ // The first pivot row found is below where it should currently be placed.
+ if (pivotRow > nowDone) {
+ equalities.swapRows(pivotRow, nowDone);
+ pivotRow = nowDone;
+ }
+
+ // Normalize all lower equations and all inequalities.
+ for (unsigned i = nowDone + 1; i < eqs; ++i) {
+ eliminateFromConstraint(this, i, pivotRow, firstVar, 0, true);
+ equalities.normalizeRow(i);
+ }
+ for (unsigned i = 0, ineqs = getNumInequalities(); i < ineqs; ++i) {
+ eliminateFromConstraint(this, i, pivotRow, firstVar, 0, false);
+ inequalities.normalizeRow(i);
+ }
+ gcdTightenInequalities();
+ }
+
+ // No redundant rows.
+ if (nowDone == eqs)
+ return false;
+
+ // Check to see if the redundant rows constant is zero, a non-zero value means
+ // the set is empty.
+ for (unsigned i = nowDone; i < eqs; ++i) {
+ if (atEq(i, vars) == 0)
+ continue;
+
+ *this = getEmpty(getSpace());
+ return true;
+ }
+ // Eliminate rows that are confined to be all zeros.
+ removeEqualityRange(nowDone, eqs);
+ return true;
+}
+
// A more complex check to eliminate redundant inequalities. Uses FourierMotzkin
// to check if a constraint is redundant.
void IntegerRelation::removeRedundantInequalities() {
@@ -1269,6 +1326,21 @@ void IntegerRelation::removeDuplicateDivs() {
divs.removeDuplicateDivs(merge);
}
+void IntegerRelation::simplify() {
+ bool changed = true;
+ // Repeat until we reach a fixed point.
+ while (changed) {
+ if (isObviouslyEmpty())
+ return;
+ changed = false;
+ normalizeConstraintsByGCD();
+ changed |= gaussianEliminate();
+ changed |= removeDuplicateConstraints();
+ }
+ // Current set is not empty.
+ return;
+}
+
/// Removes local variables using equalities. Each equality is checked if it
/// can be reduced to the form: `e = affine-expr`, where `e` is a local
/// variable and `affine-expr` is an affine expression not containing `e`.
@@ -2216,6 +2288,68 @@ IntegerPolyhedron IntegerRelation::getDomainSet() const {
return IntegerPolyhedron(std::move(copyRel));
}
+bool IntegerRelation::removeDuplicateConstraints() {
+ bool changed = false;
+ SmallDenseMap<ArrayRef<MPInt>, unsigned> hashTable;
+ unsigned ineqs = getNumInequalities(), cols = getNumCols();
+
+ if (ineqs <= 1)
+ return changed;
+
+ // Check if the non-constant part of the constraint is the same.
+ ArrayRef<MPInt> row = getInequality(0).drop_back();
+ hashTable.insert({row, 0});
+ for (unsigned k = 1; k < ineqs; ++k) {
+ row = getInequality(k).drop_back();
+ if (!hashTable.contains(row)) {
+ hashTable.insert({row, k});
+ continue;
+ }
+
+ // For identical cases, keep only the smaller part of the constant term.
+ unsigned l = hashTable[row];
+ changed = true;
+ if (atIneq(k, cols - 1) <= atIneq(l, cols - 1))
+ inequalities.swapRows(k, l);
+ removeInequality(k);
+ --k;
+ --ineqs;
+ }
+
+ // Check the neg form of each inequality, need an extra vector to store it.
+ SmallVector<MPInt> negIneq(cols - 1);
+ for (unsigned k = 0; k < ineqs; ++k) {
+ row = getInequality(k).drop_back();
+ negIneq.assign(row.begin(), row.end());
+ for (MPInt &ele : negIneq)
+ ele = -ele;
+ if (!hashTable.contains(negIneq))
+ continue;
+
+ // For cases where the neg is the same as other inequalities, check that the
+ // sum of their constant terms is positive.
+ unsigned l = hashTable[row];
+ auto sum = atIneq(l, cols - 1) + atIneq(k, cols - 1);
+ if (sum > 0 || l == k)
+ continue;
+
+ // A sum of constant terms equal to zero combines two inequalities into one
+ // equation, less than zero means the set is empty.
+ changed = true;
+ if (k < l)
+ std::swap(l, k);
+ if (sum == 0) {
+ addEquality(getInequality(k));
+ removeInequality(k);
+ removeInequality(l);
+ } else
+ *this = getEmpty(getSpace());
+ break;
+ }
+
+ return changed;
+}
+
IntegerPolyhedron IntegerRelation::getRangeSet() const {
IntegerRelation copyRel = *this;
diff --git a/mlir/lib/Analysis/Presburger/PresburgerRelation.cpp b/mlir/lib/Analysis/Presburger/PresburgerRelation.cpp
index 5a9cf71fc86793f..a82b60cddc73dac 100644
--- a/mlir/lib/Analysis/Presburger/PresburgerRelation.cpp
+++ b/mlir/lib/Analysis/Presburger/PresburgerRelation.cpp
@@ -83,19 +83,19 @@ void PresburgerRelation::unionInPlace(const IntegerRelation &disjunct) {
void PresburgerRelation::unionInPlace(const PresburgerRelation &set) {
assert(space.isCompatible(set.getSpace()) && "Spaces should match");
- if (isPlainEqual(set))
+ if (isObviouslyEqual(set))
return;
- if (isPlainEmpty()) {
+ if (isObviouslyEmpty()) {
disjuncts = set.disjuncts;
return;
}
- if (set.isPlainEmpty())
+ if (set.isObviouslyEmpty())
return;
- if (isPlainUniverse())
+ if (isObviouslyUniverse())
return;
- if (set.isPlainUniverse()) {
+ if (set.isObviouslyUniverse()) {
disjuncts = set.disjuncts;
return;
}
@@ -144,10 +144,10 @@ PresburgerRelation::intersect(const PresburgerRelation &set) const {
// If the set is empty or the other set is universe,
// directly return the set
- if (isPlainEmpty() || set.isPlainUniverse())
+ if (isObviouslyEmpty() || set.isObviouslyUniverse())
return *this;
- if (set.isPlainEmpty() || isPlainUniverse())
+ if (set.isObviouslyEmpty() || isObviouslyUniverse())
return set;
PresburgerRelation result(getSpace());
@@ -576,6 +576,9 @@ static PresburgerRelation getSetDifference(IntegerRelation b,
}
}
+ // Try to simplify the results.
+ result = result.simplify();
+
return result;
}
@@ -593,7 +596,7 @@ PresburgerRelation::subtract(const PresburgerRelation &set) const {
// If we know that the two sets are clearly equal, we can simply return the
// empty set.
- if (isPlainEqual(set))
+ if (isObviouslyEqual(set))
return result;
// We compute (U_i t_i) \ (U_i set_i) as U_i (t_i \ V_i set_i).
@@ -615,7 +618,7 @@ bool PresburgerRelation::isEqual(const PresburgerRelation &set) const {
return this->isSubsetOf(set) && set.isSubsetOf(*this);
}
-bool PresburgerRelation::isPlainEqual(const PresburgerRelation &set) const {
+bool PresburgerRelation::isObviouslyEqual(const PresburgerRelation &set) const {
if (!space.isCompatible(set.getSpace()))
return false;
@@ -625,7 +628,7 @@ bool PresburgerRelation::isPlainEqual(const PresburgerRelation &set) const {
// Compare each disjunct in this PresburgerRelation with the corresponding
// disjunct in the other PresburgerRelation.
for (unsigned int i = 0, n = getNumDisjuncts(); i < n; ++i) {
- if (!getDisjunct(i).isPlainEqual(set.getDisjunct(i)))
+ if (!getDisjunct(i).isObviouslyEqual(set.getDisjunct(i)))
return false;
}
return true;
@@ -635,10 +638,12 @@ bool PresburgerRelation::isPlainEqual(const PresburgerRelation &set) const {
/// otherwise. It is a simple check that only check if the relation has at least
/// one unconstrained disjunct, indicating the absence of constraints or
/// conditions.
-bool PresburgerRelation::isPlainUniverse() const {
- return llvm::any_of(getAllDisjuncts(), [](const IntegerRelation &disjunct) {
- return disjunct.getNumConstraints() == 0;
- });
+bool PresburgerRelation::isObviouslyUniverse() const {
+ for (const IntegerRelation &disjunct : getAllDisjuncts()) {
+ if (disjunct.getNumConstraints() == 0)
+ return true;
+ }
+ return false;
}
bool PresburgerRelation::isConvexNoLocals() const {
@@ -646,7 +651,9 @@ bool PresburgerRelation::isConvexNoLocals() const {
}
/// Return true if there is no disjunct, false otherwise.
-bool PresburgerRelation::isPlainEmpty() const { return getNumDisjuncts() == 0; }
+bool PresburgerRelation::isObviouslyEmpty() const {
+ return getNumDisjuncts() == 0;
+}
/// Return true if all the sets in the union are known to be integer empty,
/// false otherwise.
@@ -1015,6 +1022,17 @@ bool PresburgerRelation::hasOnlyDivLocals() const {
});
}
+PresburgerRelation PresburgerRelation::simplify() const {
+ PresburgerRelation origin = *this;
+ PresburgerRelation result = PresburgerRelation(getSpace());
+ for (IntegerRelation &disjunct : origin.disjuncts) {
+ disjunct.simplify();
+ if (!disjunct.isObviouslyEmpty())
+ result.unionInPlace(disjunct);
+ }
+ return result;
+}
+
void PresburgerRelation::print(raw_ostream &os) const {
os << "Number of Disjuncts: " << getNumDisjuncts() << "\n";
for (const IntegerRelation &disjunct : disjuncts) {
More information about the Mlir-commits
mailing list